Kat Troche
Dec 19, 2025 ArticleWhat happens when a star dies? In 2019, Betelgeuse dimmed in brightness, sparking speculation that it may soon explode as a supernova. While it likely won’t explode quite yet, we can preview its fate by observing the nearby Crab Nebula.
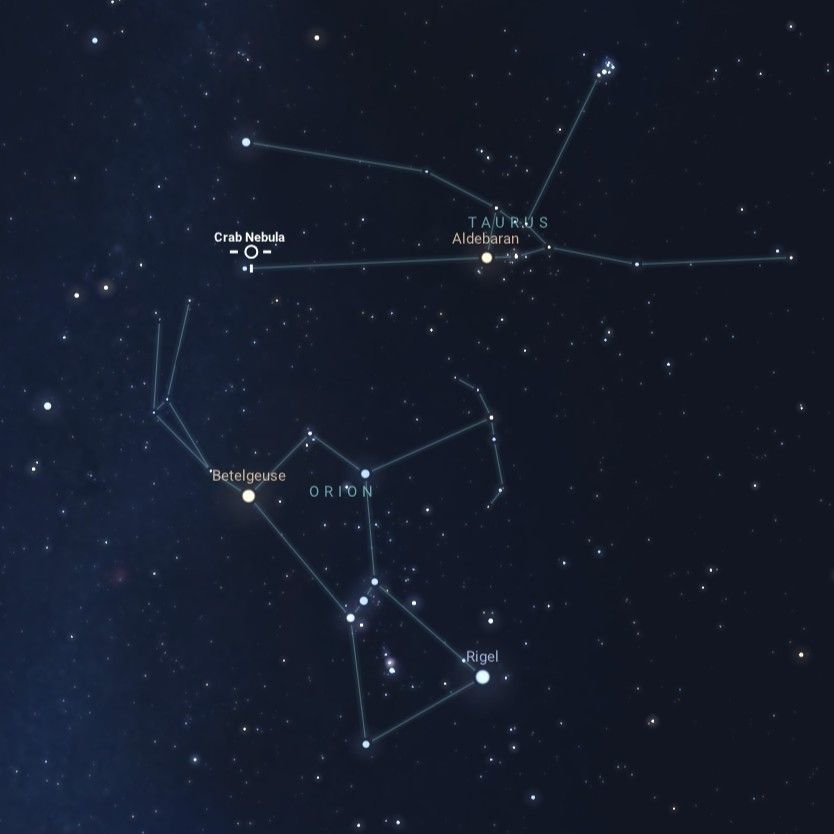
A view of the constellations Orion and Taurus, along with notable features: Betelgeuse in Orion, and Aldebaran and the Crab Nebula in Taurus.Stellarium WebBetelgeuse is easy to find as the red-hued shoulder star of Orion. A variable star, Betelgeuse, usually competes with the brilliant blue-white Rigel for the position of the brightest star in Orion. Betelgeuse is a young star, estimated to be a few million years old, but due to its giant size, it leads a fast and furious life. This massive star, known as a supergiant, exhausted the hydrogen fuel in its core and began to fuse helium instead, which caused the outer layers of the star to cool and swell dramatically in size. Betelgeuse is one of the few stars for which we have any detailed surface observations, due to its vast size – somewhere between the diameters of the orbits of Mars and Jupiter – and its relatively close distance of about 642 light-years. Betelgeuse is also a “runaway star,” with its remarkable speed possibly triggered by a merger with a smaller companion star. If that is the case, Betelgeuse may actually have millions of years left! So, Betelgeuse may not explode soon after all, or it might explode tomorrow! We have much more to learn about this intriguing star.
This image of the Crab Nebula combines data from five different telescopes: The Very Large Array (radio) in red; Spitzer Space Telescope (infrared) in yellow; Hubble Space Telescope (visible) in green; XMM-Newton (ultraviolet) in blue; and Chandra X-ray Observatory (X-ray) in purple. It is known as the expanding gaseous remnant from a star that self-detonated as a supernova, briefly shining as brightly as 400 million suns.NASA, ESA, G. Dubner (IAFE, CONICET-University of Buenos Aires) et al.; A. Loll et al.; T. Temim et al.; F. Seward et al.; VLA/NRAO/AUI/NSF; Chandra/CXC; Spitzer/JPL-Caltech; XMM-Newton/ESA; and Hubble/STScIThe Crab Nebula (M1) is relatively close to Betelgeuse in the sky, in the nearby constellation of Taurus. Its ghostly, spidery gas clouds result from a massive explosion; a supernova observed by astronomers in 1054! A backyard telescope allows you to see some details. Still, only advanced telescopes reveal the rapidly spinning neutron star found in its center: the last stellar remnant from that cataclysmic event. These gas clouds were created during the giant star’s violent demise and expand ever outward to enrich the universe with heavy elements like silicon, iron, and nickel. These element-rich clouds are like a cosmic fertilizer, making rocky planets like our own Earth possible. Supernovae also send out powerful shock waves that help trigger star formation. In fact, if it weren’t for a long-ago supernova, our solar system – along with all of us – wouldn’t exist! You can learn much more about the Crab Nebula in a video from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope: bit.ly/CrabNebulaVisual
Want to know more about the life cycle of stars? Explore stellar evolution with “The Lives of Stars” activity and handout at bit.ly/starlifeanddeath, part of our SUPERNOVA! toolkit.
Originally posted by Dave Prosper: February 2020
Last Updated by Kat Troche: December 2025